Tagged vs Untagged VLAN: What's the Difference?
In this video, we'll explain what a VLAN is, how tagged VLANs differ from untagged VLANs, and why VLAN tagging can up-level your network security.
Learn more about:
Untagged vs Tagged VLAN: https://jumpcloud.com/blog/untagged-vs-tagged-vlan?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Cloud RADIUS: https://jumpcloud.com/platform/cloud-radius?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Try JumpCloud for free: https://jumpcloud.com/signup?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Resources and social media:
Blog: https://jumpcloud.com/blog?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Community: https://community.jumpcloud.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/JumpCloud.DaaS/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/JumpCloud
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/jumpcloud
#jumpcloud #vlan
Transcript:
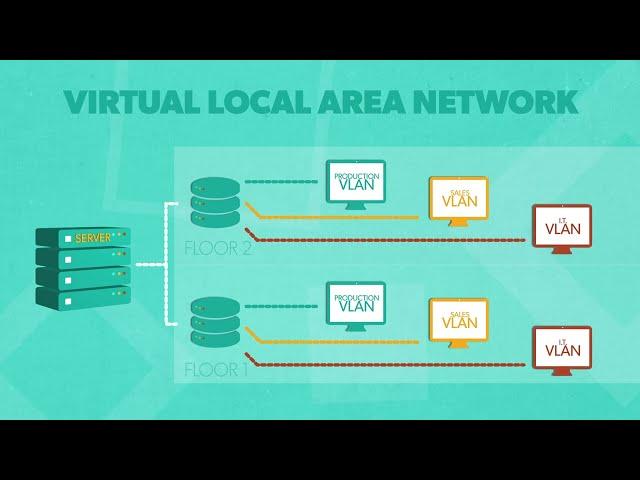
What is a VLAN? A VLAN or virtual area network is a group of devices that share a broadcast domain. Instead of making all devices in a network process and accept a broadcast, VLANs separate local area networks into distinct segments, typically one for every department. Devices within a VLAN can communicate with each other and each other only.
They store rules about how sub-networks can communicate in access ports, which are classified as tagged or untagged. Untagged or access VLANs are connected to hosts, usually servers that pass VLAN information to and from each network, and cannot differentiate between any VLAN configuration.
In this way, untagged VLANs have a more linear structure, moving from A to B rather than from A to B, C, and D. Generally, untagged VLANs are the default. Tagged or trunk VLANs enable switch access ports to handle more than one VLAN and separate traffic accordingly.
Instead of the data going from one host to another, frames with a VLAN tag can be distributed from one host to many other hosts that are connected to a port, depending on their configuration.
The tags denote which packets should be sent to specific VLANs on the other side. Tagging makes for a more involved VLAN implementation, but it also provides a wide range of benefits, such as stronger security. Identifier tags can be weaved into the user authentication process automatically and dynamically, steering users into the proper VLAN. Tagging also leads to less congestion. By pre-configuring traffic direction, networks are more efficient and eliminate the need for costly devices. IT has visibility into VLAN tags as well, making it easier for them to understand the root cause of any issues and make updates on the fly.
Although VLAN tagging takes more advanced preparation and configuration, it's optimal for companies with sensitive data, high traffic, and multiple VLANs. Curious about what JumpCloud can do for your network security? JumpCloud's cloud model for RADIUS allows IT to provision and deprovision user access to VPN and WiFi networks, straight from their browser, and further secure those networks with MFA without the restriction of building, maintaining, or monitoring physical servers. Subscribe to our YouTube channel to stay up to date on the latest and greatest security solutions.
Learn more about:
Untagged vs Tagged VLAN: https://jumpcloud.com/blog/untagged-vs-tagged-vlan?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Cloud RADIUS: https://jumpcloud.com/platform/cloud-radius?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Try JumpCloud for free: https://jumpcloud.com/signup?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Resources and social media:
Blog: https://jumpcloud.com/blog?utm_source=youtube-organic&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=tagged-vs-untagged-vlan
Community: https://community.jumpcloud.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/JumpCloud.DaaS/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/JumpCloud
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/jumpcloud
#jumpcloud #vlan
Transcript:
What is a VLAN? A VLAN or virtual area network is a group of devices that share a broadcast domain. Instead of making all devices in a network process and accept a broadcast, VLANs separate local area networks into distinct segments, typically one for every department. Devices within a VLAN can communicate with each other and each other only.
They store rules about how sub-networks can communicate in access ports, which are classified as tagged or untagged. Untagged or access VLANs are connected to hosts, usually servers that pass VLAN information to and from each network, and cannot differentiate between any VLAN configuration.
In this way, untagged VLANs have a more linear structure, moving from A to B rather than from A to B, C, and D. Generally, untagged VLANs are the default. Tagged or trunk VLANs enable switch access ports to handle more than one VLAN and separate traffic accordingly.
Instead of the data going from one host to another, frames with a VLAN tag can be distributed from one host to many other hosts that are connected to a port, depending on their configuration.
The tags denote which packets should be sent to specific VLANs on the other side. Tagging makes for a more involved VLAN implementation, but it also provides a wide range of benefits, such as stronger security. Identifier tags can be weaved into the user authentication process automatically and dynamically, steering users into the proper VLAN. Tagging also leads to less congestion. By pre-configuring traffic direction, networks are more efficient and eliminate the need for costly devices. IT has visibility into VLAN tags as well, making it easier for them to understand the root cause of any issues and make updates on the fly.
Although VLAN tagging takes more advanced preparation and configuration, it's optimal for companies with sensitive data, high traffic, and multiple VLANs. Curious about what JumpCloud can do for your network security? JumpCloud's cloud model for RADIUS allows IT to provision and deprovision user access to VPN and WiFi networks, straight from their browser, and further secure those networks with MFA without the restriction of building, maintaining, or monitoring physical servers. Subscribe to our YouTube channel to stay up to date on the latest and greatest security solutions.
Тэги:
#jumpcloud #vlan #virtual_local_area_network #tagged_vlan #untagged_vlanКомментарии:
【2025/4月】炎炎消防隊 第三季 -「先導PV」【MCE漢化組】
AWSL動漫預告 Anime News
Наоми дразнит своей киской Белфорта Волк с Уолл стрит 2013 HD
Amazing MomentsHD